Special Topic: Stellar Intruders
Five weeks ago I devoted the “Special Topics” presentation to the subject of the Oort Cloud, the large spherical cloud of comets that is believed to enshroud the solar system out to distances of several tens of thousands of Astronomical Units. The comets in the Oort Cloud have been there since the forming Jupiter and …
This Week in History: February 9-15
FEBRUARY 9, 1986: During its most recent return Comet 1P/Halley passes through perihelion at a heliocentric distance of 0.587 AU. Comet Halley’s 1986 return is a future “Comet of the Week,” and its entire history is the subject of a future “Special Topics” presentation. FEBRUARY 10, 1907: August Kopff at Heidelberg Observatory in Germany discovers …
Comet of the Week: PANSTARRS C/2017 T2
Perihelion: 2020 May 4.95, q = 1.615 AU After devoting my “Comet of the Week” last week to the first comet I ever observed, it seems appropriate to devote this week’s “Comet of the Week” to the brightest comet that is currently visible in our nighttime skies, and which is easily accessible for observations, at …
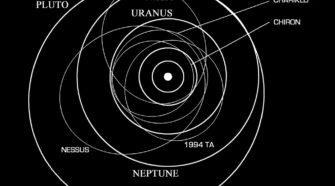
Special Topic: Centaurs
In previous “Special Topics” presentations I have focused on asteroid populations in the “main asteroid belt” between Mars and Jupiter, and on asteroids in near-Earth space. If, however, as is now widely believed to be the case, asteroids are among the “leftovers” of the planet formation process, we would accordingly expect asteroids to exist in …
This Week in History: February 2-8
FEBRUARY 2, 1106: Sky-watchers around the world see a brilliant comet during the daytime hours. In subsequent days it becomes visible in the evening sky, initially very bright with an extremely long tail, and although it faded rapidly it remained visible until mid-March. The available information is not enough to allow a valid orbit calculation, but …
Comet of the Week: Tago-Sato-Kosaka 1969g
Perihelion: 1969 December 21.27, q = 0.473 AU Everyone fondly remembers their “first.” When it comes to comets, my “first” came exactly 50 years ago on Monday evening, February 2, 1970, when I was 11 years old and in the 6th Grade, and involved a 5th-magnitude fuzzball located close to the 2nd-magnitude star Hamal in …